We are a “coalition-of-the-willing” of industry, British Columbia (BC) government and academic stakeholders committed to decarbonising long-distance transport in British Columbia and beyond.
The British Columbia Sustainable Marine, Aviation, Rail and Trucking (BC-SMART) Consortium encourages the production and use of low carbon intensity fuels for long-distance transport.
Climate change has become strikingly obvious over the recent decades with increased global average temperatures and extreme weather events. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) there is more than 95% probability that anthropogenic Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emissions are responsible for the increase in global temperatures. Consequently, we are at a crossroads to take big and bold action to minimize GHG emissions from all aspects of our lives.
Globally, transportation accounts for about 14% of GHG emissions where long-distance transport sectors including aviation, marine, rail and trucking are key contributors. For example, the aviation sector is responsible for about 2% of global emissions while marine shipping contributes 2-3% of global CO2 emissions. With rapid economic expansions in Asia and countries such as Brazil, long-distance transportation-derived GHG emissions are expected to grow substantially.
Long-distance transport needs sector-compatible, low carbon intensity (low CI) renewable fuels

While electrification and other technologies can decarbonise urban transport, they are not viable short-term (2030-horizon) options for long-distance transport sectors. Marine, aviation, rail and long-distance trucking require sector-compatible, low carbon intensity renewable fuels. We believe drop-in biofuels to be a clean solution in the near-term.
British Columbia Advantage
The province of British Columbia (BC) is a key logistic hub that links Western Canada including the Canadian Prairies to regional and international markets by road, rail, water and air. It is historically considered North America’s Pacific Gateway to Asia and is also part of the Cascadia Innovation Corridor that focuses on shared development in research, commerce and transportation across the Pacific Northwest.
BC is uniquely positioned to champion low CI fuels:
Forests and other feedstocks: BC is home to 55 million hectares (18% of Canadian forest cover) of sustainably managed forests. As such, large volumes of forest and sawmill residues, non-sawlog/non-merchant timbers within merchantable forest stands and wood pellets are potentially available for conversion into low CI biofuels. Moreover, BC maintains a well-established supply chain for collecting, transporting and densifying forest/saw mill residues.
Moreover, large volumes of potential lipid/oleochemical/biomass (pellets/chips) feedstocks/intermediates that can be utilized to produce biofuels pass through the Port of Vancouver each year.
Favourable policy landscape: A carbon tax on fossil fuels has been in effect since 2008 in the province. BC also leads the way in policy drivers such as low carbon fuel standard (LCFS). Collectively, these tools help bridge the short-term price gap between biofuels and fossil fuels.
Industry champions: BC is home to pioneering industry sectors spanning passenger and cargo transport, feedstock processing and oil refining that are committed to low CI fuels.
By Sea, Land and Air We Prosper
The fact that long-distance transport sectors including marine, aviation, rail and trucking play a vital role in BC’s economy underscores the need for low CI fuels that satisfy the unique requirements of these sectors.
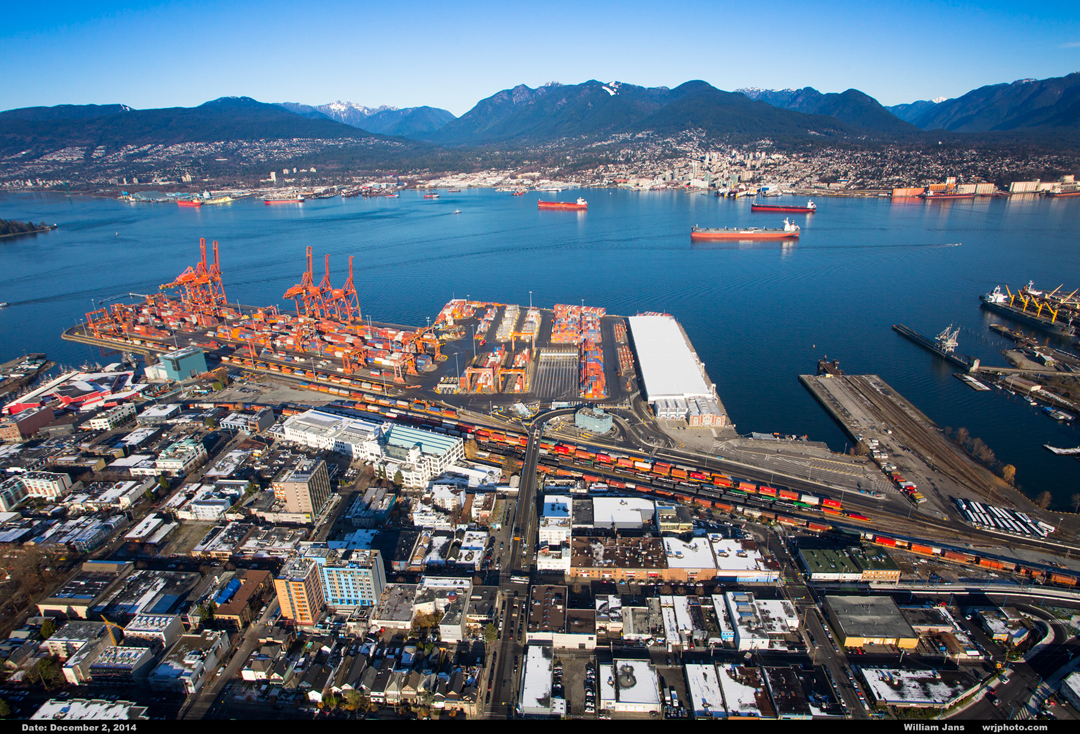

$200 billion annual trade with over 170 economies
photo credit: Vancouver Fraser Port Authority



Our Mission
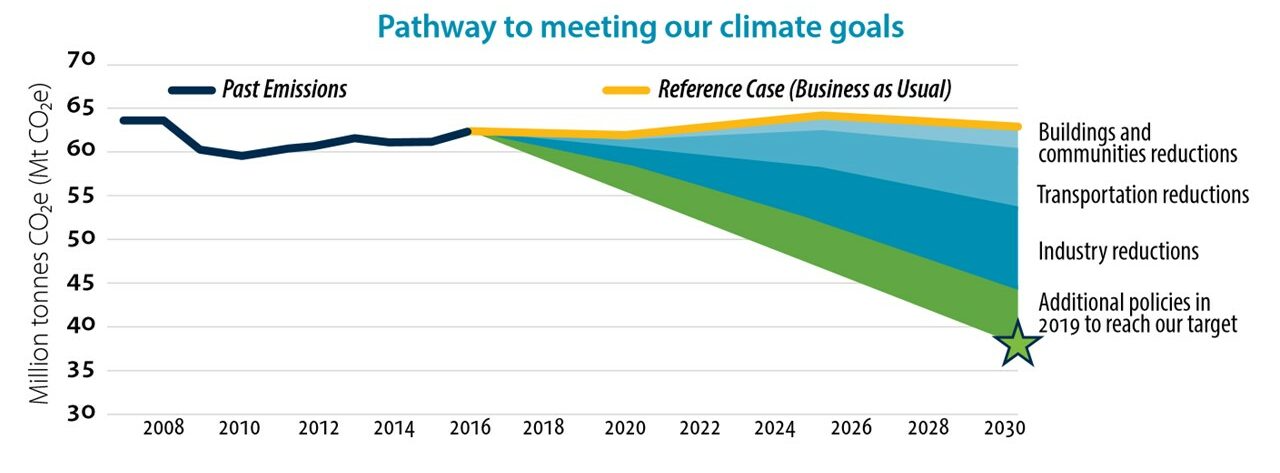
The BC-SMART Low Carbon Fuels Consortium strives to help deliver the BC government’s CleanBC GHG emission targets by developing Sustainable, low-carbon intensity fuels for long-distance transportation sectors, including Marine, Aviation, Rail and long-distance Trucking (SMART)
Committed to the CleanBC plan
In 2018, the BC government introduced the CleanBC strategic plan setting the following targets for 2030:
- 18.9 million ton reduction in GHG emissions
- 20% low carbon fuel standard
- 650 million litre annual renewable fuel production (about 8% of fuel use in the province)
Most importantly CleanBC calls for these targets to be met while creating jobs and driving economic growth in the province.
About 30% of emission reductions are expected to be realized through a cleaner transportation sector driven by a switch to cleaner fuels and the adoption of zero-emission vehicles.

Decarbonising Long-Distance Transport
Supported by:





